Overview
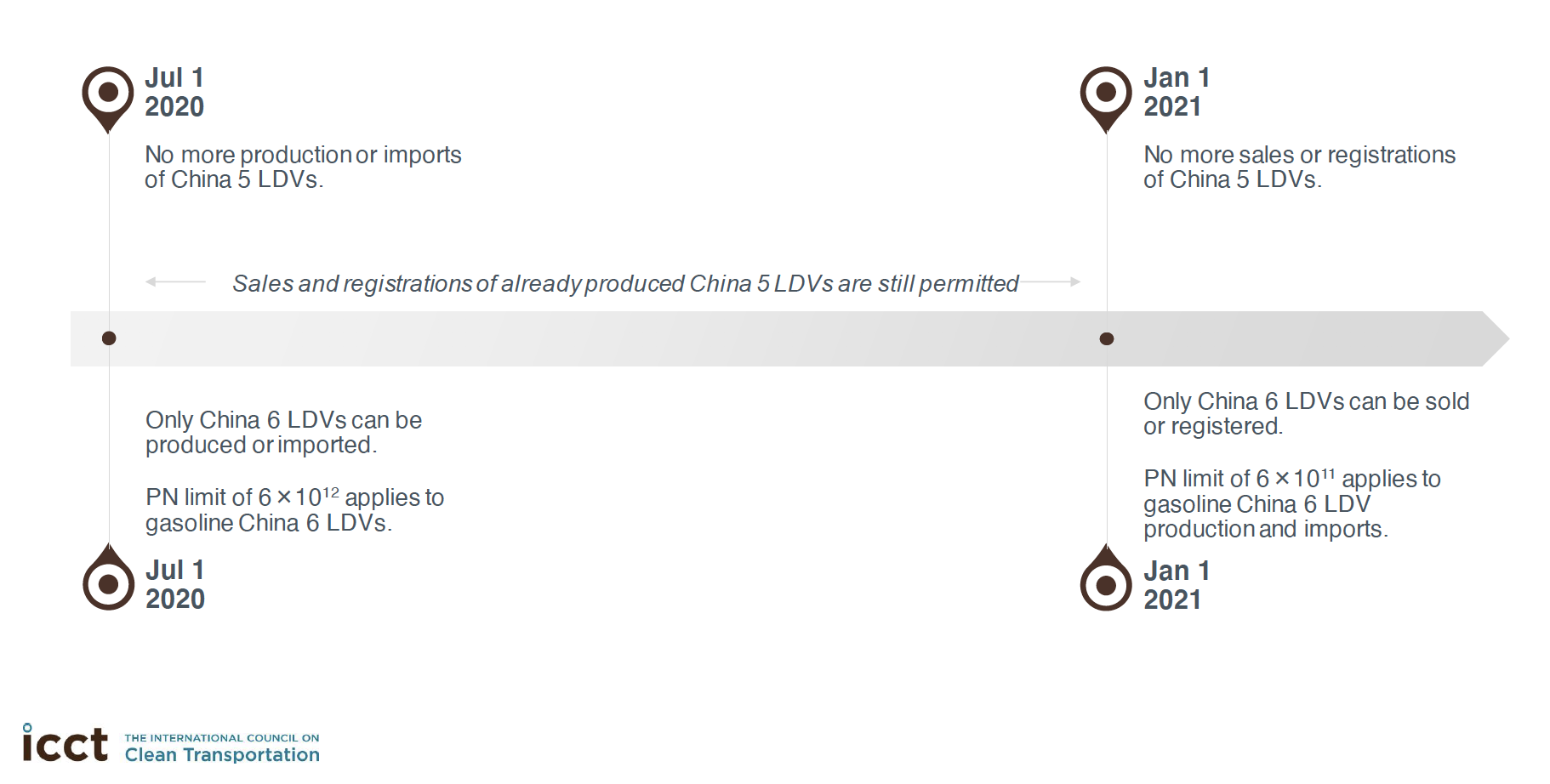
On April 30th, 2020, China decided to delay the implementation of the final particle number (PN) limit in China 6 for six months (until January 2021) nationwide. China will also allow continued sales and registration of in-stock China 5 cars for the same period, in regions that have not adopted China 6 in advance of the national implementation schedule. By April 2020, 16 regions, including Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Chongqing, Hebei, Henan, Guangdong, Shandong, Hainan, Anhui, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu, as well as central cities of Shanxi, Shaanxi, Sichuan, and Neimenggu, had all implemented China 6.
Conventional pollutant emission limits
Regulating Body
Nationwide: Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE, formerly the Ministry of Environmental Protection)
Regional and Local: Ecology and Environment Bureaus
Nationwide: China 5 (similar to Euro 5), GB 18352.5-2013
All vehicles in categories M1, M2, and N1 with a reference mass not exceeding 3500kg. Categories are based on European precedent with some minor differences (see below).
History
Nationwide Standards
China’s current nationwide light-duty vehicle emission standard is China 5 (Euro 5). In December 2016, the Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP) issued the final version of the China 6 standard for both gasoline and diesel vehicles. The China 6 standard, with implementation dates of 1 July 2020 for China 6a and 1 July 2023 for China 6b, is one of the most stringent emission standards around the world.
Due to declining car sales since mid-2019, and the Coronavirus outbreak and subsequent lockdown in 2020, China decided to delay the implementation date of the final PN limit in China 6 (6 x 10^11) for six months nationwide. The implementation will now go into effect in January 2021. China will also allow continued sales and registration of in-stock China 5 cars for the same period, in regions that have not adopted China 6 in advance of the national implementation schedule (by April 2020, Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Chongqing, Hebei, Henan, Guangdong, Shandong, Hainan, Anhui, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu, as well as central cities of Shanxi, Shaanxi, Sichuan, and Neimenggu, had all implemented China 6).
The following table presents China’s light-duty vehicle emission standards implementation dates:
| Stage | Standard | Implementation Date (type approvals) |
Implementation Date (all vehicle sales and registrations) |
|---|---|---|---|
| China 1 | GB 18352.1-2001 | 1 Jan 2000 (Type 1) 1 Jan 2001 (Type 2) |
1 Jul 2000 (Type 1) 1 Oct 2001 (Type 2) |
| China 2 | GB18352.2-2001 | 1 Jul 2004 (Type 1) 1 Jul 2005 (Type 2) |
1 Jul 2005 (Type 1) 1 Jul 2006 (Type 2) |
| China 3 | GB 18352.3-2005 | 1 Jul 2007 (no EOBD req.) 1 Jul 2008 (EOBD req. for Type 1) 1 Jul 2010 (EOBD req. for all others) |
1 Jul 2008 (no EOBD req.) 1 Jul 2009 (EOBD req. for Type 1) 1 Jul 2011 (EOBD req. for all others) |
| China 4 | 1 Jul 2010 | 1 July 2011 (gasoline) 1 Jul 2013 (diesel)1 |
|
| China 5 | GB 18352.5-2013 | 1 Jan 2016 (gasoline) 1 Jan 2017 (diesel) |
1 Jan 2017 (gasoline)2 1 Jan 2018 (diesel)2 |
| China 6 | GB 18352.5-2016 | n/a | 1 Jul 2020 (China 6a)3 1 Jul 2023 (China 6b) |
| (1) This date represents a two-year delay from the date specified in the original standard. (2) The implementation date of the China 5 light-duty gasoline vehicle and light-duty diesel bus standard was 1 April 2016 in the eastern 11 provinces (Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Liaoning, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Shandong, Guangdong, and Hainan). (3) Sales and registration of in-stock China 5 LDVs are allowed in regions that have not yet adopted China 6 until January 1, 2021. By April 2020, Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, Chongqing, Hebei, Henan, Guangdong, Shandong, Hainan, Anhui, Zhejiang, and Jiangsu, as well as central cities of Shanxi, Shaanxi, Sichuan, and Neimenggu, had all implemented China 6. |
|||
Regional Standards
Once a nationwide standard has been issued, cities and regions in China may implement the standard in advance of the nationwide implementation dates, conditional on receiving approval from the State Council. Beijing has historically been China’s leader in aggressively implementing new standards, followed by Shanghai, Guangzhou, and some other cities.
In early 2013, because the China 5 national standard was not yet released, Beijing was granted special approval to adopt a custom “Beijing 5” standard. Shanghai implemented the national China 5 standard early in 2014.
By April 2020, 16 cities and provinces had implemented either China 6a or 6b (see table below). Collectively, these jurisdictions represent over 70% of the national market.
| Province | City | Vehicle Category | Sub-category | Fuel Type | Standard Stage | Effective Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | Beijing | LDV | All | Petrol | 6b | Jan-20 |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | LDV | All | All | 6b | Jul-19 |
| Tianjin | Tianjin | LDV | All | All | 6b | Jul-19 |
| Chongqing | Chongqing | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Hebei | All | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Henan | All | LDV | All | All | 6a or 6b | Jul-19 |
| Guangdong | All | LDV | All | All | 6b | Jul-19 |
| Shandong | All | LDV | All | All | 6a or 6b | Jul-19 |
| Shanxi | Eight cities | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Hainan | All | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Anhui | All | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Shaanxi | Six cities and two districts | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Sichuan | 15 cities | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Zhejiang | All | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Jiangsu | All | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Neimenggu | Six cities | LDV | All | All | 6a | Jul-19 |
| Stage | Beijing | Shanghai | Guangzhou and others |
|---|---|---|---|
| China 1 | 1 Jan 1999 | 1 Jul 1999 | n/a |
| China 2 | 1 Jan 2003 | 1 Mar 2003 | 1 Jul 2005 |
| China 3 | 31 Dec 2005 | HDV: phased-in over 2007 | 1 Sep 2006 |
| China 4 | LDV: 1 Dec 2008 (OBD req.) HDV: 1 Jul 2008 |
1 Nov 2009 | 1 Jun 2010 (GZ + 9 cities in Guangdong Province) |
| China 5 | 1 Feb 20131 | 1 May 2014 | 31 Dec 2015 (GZ + 8 cities in Guangdong Province) 30 Jun 2016 Guangdong Province Apr 1 2016 (gasoline, and light-duty diesel bus) 11 Eastern provinces2 |
| (1) Technically the “Beijing 5” standard, as the nationwide China 5 standard had not yet been released when it was implemented. (2) These 11 eastern provinces are Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Liaoning, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Shandong, Guangdong, and Hainan. |
|||
Technical Standards
Vehicle Classification
Light-duty vehicle categories are based on the EU classification with some deviations:
- Type 1 vehicles: M1 vehicles for no more than 6 passengers including the driver, and GVWR ≤ 2.5 tons.
- Type 2 vehicles: Other light-duty vehicles (including N1 light commercial vehicles) are further divided into three classes based on the reference mass.
Limit Values
Emission limits for China III, IV, 5, and 6 are shown below. (Note: the official English titles of China III and IV use Roman numerals, while the official English title of China 5 and 6 use Arabic numerals.) Starting with China 6a, regulated emission limits are fuel-neutral, meaning the same limits are applied to gasoline and diesel vehicles.
| Engine Type | Stage | Vehicle Type | Level | Reference Mass | CO | HC | NMHC | HC+NOx | NOx | N2O | PM(1) | PN(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kg | g/km | #/km | ||||||||||
| Spark Ignition (Gasoline) |
China III | 1 | – | All | 2.30 | 0.20 | – | – | 0.15 | – | – | – |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 2.30 | 0.20 | – | – | 0.15 | – | – | – | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 4.17 | 0.25 | – | – | 0.18 | – | – | – | |||
| III | >1760 | 5.22 | 0.29 | – | – | 0.21 | – | – | – | |||
| China IV | 1 | – | All | 1.00 | 0.10 | – | – | 0.08 | – | – | – | |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 1.00 | 0.10 | – | – | 0.08 | – | – | – | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 1.81 | 0.13 | – | – | 0.10 | – | – | – | |||
| III | >1760 | 2.27 | 0.16 | – | – | 0.11 | – | – | – | |||
| China 5 | 1 | – | All | 1.00 | 0.10 | – | – | 0.06 | – | 0.0045 | – | |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 1.00 | 0.10 | – | – | 0.06 | – | 0.0045 | – | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 1.81 | 0.13 | – | – | 0.075 | – | 0.0045 | – | |||
| III | >1760 | 2.27 | 0.16 | – | – | 0.082 | – | 0.0045 | – | |||
| China 6a | 1 | – | All | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.068 | – | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.068 | – | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 0.88 | 0.13 | 0.09 | – | 0.075 | 0.025 | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| III | >1760 | 1 | 0.16 | 0.108 | – | 0.082 | 0.03 | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| China 6b | 1 | – | All | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.035 | – | 0.035 | 0.02 | 0.003 | 6.0×1011 | |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.035 | – | 0.035 | 0.02 | 0.003 | 6.0×1011 | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 0.63 | 0.065 | 0.045 | – | 0.045 | 0.025 | 0.003 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| III | >1760 | 0.74 | 0.08 | 0.055 | – | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| Compression Ignition (Diesel) |
China III | 1 | – | All | 0.64 | – | – | 0.56 | 0.50 | – | 0.050 | – |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 0.64 | – | – | 0.56 | 0.50 | – | 0.050 | – | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 0.80 | – | – | 0.72 | 0.65 | – | 0.070 | – | |||
| III | >1760 | 0.95 | – | – | 0.86 | 0.78 | – | 0.100 | – | |||
| China IV | 1 | – | All | 0.50 | – | – | 0.30 | 0.25 | – | 0.025 | – | |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 0.50 | – | – | 0.30 | 0.25 | – | 0.025 | – | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 0.63 | – | – | 0.39 | 0.33 | – | 0.040 | – | |||
| III | >1760 | 0.74 | – | – | 0.46 | 0.39 | – | 0.060 | – | |||
| China 5 | 1 | – | All | 0.50 | – | – | 0.23 | 0.18 | – | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 0.50 | – | – | 0.23 | 0.18 | – | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 0.63 | – | – | 0.295 | 0.235 | – | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| III | >1760 | 0.74 | – | – | 0.35 | 0.28 | – | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| China 6a | 1 | – | All | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.068 | – | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.068 | – | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 0.88 | 0.13 | 0.09 | – | 0.075 | 0.025 | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| III | >1760 | 1 | 0.16 | 0.108 | – | 0.082 | 0.03 | 0.0045 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| China 6b | 1 | – | All | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.035 | – | 0.035 | 0.02 | 0.003 | 6.0×1011 | |
| 2 | I | <1305 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.035 | – | 0.035 | 0.02 | 0.003 | 6.0×1011 | ||
| II | 1305-1760 | 0.63 | 0.065 | 0.045 | – | 0.045 | 0.025 | 0.003 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| III | >1760 | 0.74 | 0.08 | 0.055 | – | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.003 | 6.0×1011 | |||
| (1) PM limits for China 5 gasoline vehicles only apply to GDI vehicles. (2) Before Jan 1, 2021, a transitioning PN limit of 6.0×1012 #/km applies to gasoline cars. |
||||||||||||
Additional Notes and Requirements
- Chinese test cycles are based on the European test cycles (NEDC) for China I-5, and World Harmonized Light Vehicle Test Procedures (WLTP) for China 6.
- New gasoline vehicles must also meet an evaporative emission limit of 2 g/test (SHED).
- Durability requirements are 80,000 km for China III, 100,000 km for China IV, 160,000 km for China 5 and 6a, and 200,000 km for China 6b.
Real driving emission testing (RDE)
The China 6 standard includes RDE testing during both vehicle prototype and in-service stages. The emission limits for RDE tests are set as Not-To-Exceed (NTE) limits expressed as the product of a conformity factor (CF) and emission limits in Type I testing. The China 6 RDE provision is primarily based on the Euro 6 RDE package #2 passed in March 2016 with a few enhancements and modifications for the Chinese context. For NOX and PN, there are only monitoring and recording requirements before July 2023; CFs will be enforced starting from July 2023. The CFs of NOX and PN are temporarily set at 2.1 and will be reevaluated by July 2022. CO will be monitored in RDE tests, but no CFs have been set thus far. For passenger cars, for example, this leads to NTE limits of 73.5 mg/km for NOX and 1.26 x 1012 #/km for PN, which will apply once China 6b takes effect in July 2023. China 6 also extends the altitude boundary condition to 2,400 meters (m) compared 1,300 m for Euro 6 RDE. Accordingly the second-by-second emission results of RDE tests at extended high-altitude (1,300 – 2,400 m) will be divided by a factor of 1.8 when integrated into the RDE test results.
The table below provides a detailed comparison of the requirements and design of the RDE tests between China 6 and Euro 6 RDE requirements (package #3 passed in December 2016). The differences are denoted in italics.
| Requirement | Euro 6 | China 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Application | Type Approval Test | Yes | Yes |
| In-Service Test | No | Yes | |
| Emission standard | Regulated pollutants | NOX and PN after monitoring period Monitoring for CO |
|
| Binding limits in Type I test(1) | NOX: Diesel: 0.08 g/km Gasoline: 0.06 g/km PN: 6 x 1011 #/km |
Fuel-neutral NOX: 0.035 g/km PN: 6 x 1011 #/km |
|
| Conformity factor(2) (effective date) |
New types: 2.1 (9/1/2017) All new: 2.1 (9/1/2019) New types: 1.5 (1/1/2020) All new: 1.5 (1/1/2021)(3) |
All new: 2.1 (7/1/2023) | |
| Cold starts | Included | Excluded | |
| Trip requirement | Total trip duration | 90 – 120 min | |
| Minimum distance for each segment | Urban: 16 km, Rural: 16 km, Motorway: 16 km | ||
| Trip composition | Urban: 29%-44% of total distance Rural: 23%-43% of total distance Motorway: 23%-43% of total distance |
||
| Average speed | Urban: 15-40 km/h, Rural: 60-90 km/h, Motorway: >90 km/h | ||
| Stop percentage during urban segment | 6%-30% | ||
| Maximum speed during motorway segment | 145 km/h (and 160 km/h for up to 3% of motorway driving time) | 120 km/h (and 135 km/h for up to 3% of motorway driving time) | |
| High speed duration during motorway segment | At least 5 min driving at >100km/h speed | ||
| Boundary condition | Ambient temperature | Before 1/1/2020 (for new types) and 1/1/2021 (for all new vehicles): Moderate: 3°C – 30°C Extended: -2°C – 3°C and 30°C – 35°CAfterward: Moderate: 0°C -30°C Extended: -7°C -0°C, 30°C -35°C |
Moderate: 0°C -30°C Extended: -7°C -0°C, 30°C -35°C |
| Altitude | Moderate: <700 m Extended: 700-1300 m |
Moderate: <700 m Extended: 700-1300 m Further extended: 1300-2400 m |
|
| Correction factor | Extended: 1.6 | Extended: 1.6 Further extended: 1.8 |
|
| Altitude requirements | Start and end point shall not differ more than 100 m in altitude; maximum cumulative altitude increase: 1200 m over a distance of 100 km | ||
| Dynamic requirements | For each segment, max. limit is defined as the 95th percentile of v*a (speed * positive acceleration); min. limit is defined by relative positive acceleration (RPA) | ||
| Use of auxiliary systems | Optional | ||
| Evaluation methods | Data evaluation methods | Moving Average Window method or Power binning method | Moving Average Window method |
| Verification of test normality in EMROAD method | Maximum primary tolerance for the CO2characteristic curve: 30% | Maximum primary tolerance for the CO2characteristic curve: 50% | |
| (1) Type I test: exhaust emissions test after a cold start at normal ambient temperature. The emission limits in this table are for M1 and M2 vehicles in the EU and M1 Category I vehicles in China. (2) For the whole trip and for the urban segment separately. (3) N1 classes 2 and 3, and N2 vehicles are always 1 year later than the dates listed above. |
|||
Links
Regulatory documents
-
- China I: GB 18352.1-2001
- China II: GB18352.2-2001
- China III/IV: GB 18352.3-2005 (China IV for light-duty diesel extended by two years)
- China 5: 18352.5-2013
- China 6: 18352.5-2016
- Idling emissions: GB 18285-2005
- Exhaust smoke: GB 3847-2005 (diesel only)
- Beijing 5: DB11/946—2013
Other information
China takes measures to boost auto sales
Announcement on Adjusting Requirements for the Implementation of China 6 Light-duty Vehicles Emission Standard
Why China should not postpone implementation of the China 6 emission standard for new cars
China’s Stage 6 emission standard for new light-duty vehicles (final rule)
Further information: China LDV emission standards

